|
The addition of vectors by calculation or scale drawing. |
Calculations will be limited
to two perpendicular vectors. |
Don't forget to use the interactive XL spreadsheet on vectors and projectiles |
|
The resolution of vectors into two components at right angles to each other; |
Examples should include the components of forces along and perpendicular to an inclined plane. |
Note that the data sheet does NOT give you the basic trig info. You need to KNOW that!
Also you need to know Pythagoras' Theorem |
|
Conditions for equilibrium for two or three coplanar forces acting at a point;
|
Problems may be solved either by using resolved forces or by using a closed
triangle. |
|
Moments |
Moment of a force about a point defined as force × perpendicular distance from the point to the line of action of the force; torque. |
|
moment = Fd
Don't forget the interactive XL spreadsheet on moments |
|
Couple of a pair of equal and opposite forces defined as force × perpendicular
distance between the lines of action of the forces.
|
|
|
|
The principle of moments and its applications in simple balanced situations. |
|
For equilibrium:
Σ clockwise moments = Σ anticlockwise moments |
|
Centre of mass |
Calculations of the position of the centre of mass of a regular lamina are not expected. |
|
Motion along a straight line |
Displacement, speed, |
|
You met speed at KS3 |
|
velocity |
|
|
|
and acceleration. |
|
|
|
Representation by graphical methods of uniform and non-uniform acceleration;
|
|
You need to know the dynamics graphs that you met at GCSE
You have to know how to draw graphs to a high standard - and how to find gradients and areas under graphs (differentiation and integration will not be called for) |
|
Interpretation of velocity-time and displacement-time graphs for uniform and non-uniform acceleration; |
Need to understand the physical significance of areas under graph lines and gradients. |
Area under a v/t graph between two times is the distance travelled in that time interval
Gradient of s/t graph is velocity and gradient of a/t graph is acceleration |
Equations for uniform acceleration |
|
|
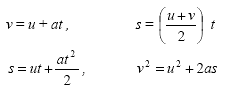
Don't forget the interactive XL Spreadsheets |
|
Acceleration due to gravity, g;
|
Detailed experimental methods of measuring 'g' are not required. |
|
|
Terminal speed |
|
You did this at GCSE... |
|
Independence of vertical and horizontal motion; |
Problems will be soluble from first
principles. The memorising of projectile equations is not required. |
Don't forget the interactive XL Spreadsheets |
|
Knowledge and application of the three laws of motion in appropriate situations.
|
|
You met these at GCSE
Make sure you can quote them!
But note that Ft = Δmv is on the A2 syllabus not the AS one!
as is conservation of momentum - so don't worry about it at AS! |
|
For constant mass, |
|
F = ma
Interactive XL Spreadsheet |
|
|
|
 |
Conservation of energy |
Principle of conservation of energy, |
Applied to examples involving gravitational
potential energy, kinetic energy and work done against resistive forces - such as friction and air resistance. |
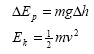 |


