GCSE Questions: Forces
Q31. Speed limits on roads increase safety.
The braking distance of a car increases as the speed of the car increases.
(a) Give two other factors that increase the braking distance of a car.
Any two from: 

 wet / icy road conditions
wet / icy road conditions
 poor condition of brakes
poor condition of brakes
 poor condition of tyres
poor condition of tyres
 increased mass of car
increased mass of car
 negative gradient of the road
negative gradient of the road
[2 marks]
(b) Explain why the driver's reaction time affects the thinking distance of a car.
Distance is the product of speed and time, 
so a longer reaction time will result in a longer distance. 
[2 marks]
(c) Scientists have investigated how drinking alcohol affects a person’s reaction time.
The graph shows the results of the investigation.
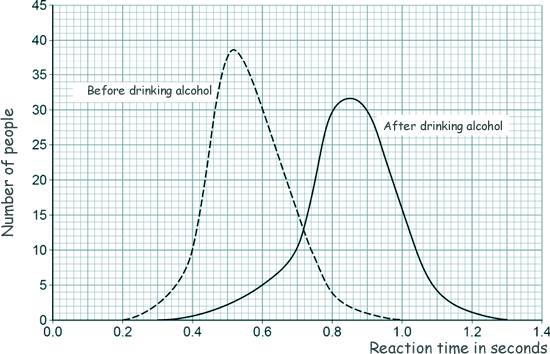
Which of the following conclusions can be made from the graph?
Tick two boxes:
| Every person's reaction time increases after drinking alcohol. |
|
| Mean reaction time increases after drinking alcohol. |
 |
| Some people's reaction time is not affected by drinking alcohol. |
|
| The change in reaction time is not the same for all people after drinking alcohol. |
 |
| There is a smaller range of reaction times after drinking alcohol. |
|
[2 marks]
(d) The diagram shows some speed cameras on a road.
The speed cameras determine the average speed of cars on the road.
The speed limit on the road shown below is 20 m/s. The cameras in are 1.5 km apart.
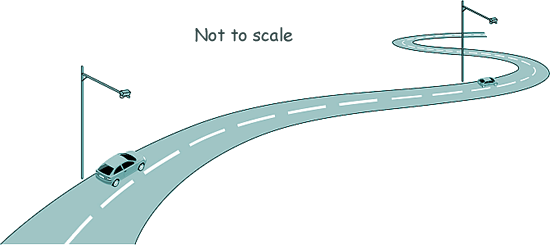
(i) Calculate the minimum time it takes to travel 1.5 km without breaking the speed limit.
distance = 1.5 km = 1500 m 
distance = speed × time
1500 = 20 × t
t = 1500/20 
t = 75  s
s 
[4 marks]
(ii) Explain why the average speed of a car between the cameras and the average velocity of the car between the cameras are different.
Velocity is a vector and therefore has magnitude and direction whereas speed is a scalar and only has magnitude. 
The road is not straight therefore the direction of the car changes during the journey,  so the velocity changes due to orientation.
so the velocity changes due to orientation.
[3 marks]
[13 Marks TOTAL]








