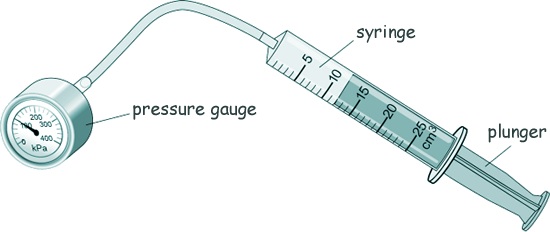
GCSE Questions: Kinetic Theory - Gases Q5. A teacher demonstrated the relationship between the pressure in a gas and the volume of the gas. The diagram shows the equipment used.
(a) What is the range of the syringe? 0 - 25 cm3 [1 mark] (b) Boyle's Law says that the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas is given by the equation: pressure × volume = constant But for this to be true two factors must remain constant - name those two factors. The mass of gas [2 marks] (c) The initial volume of the gas in the syringe was 12 cm3. The initial pressure of the gas in the syringe was 101 000 Pa. Calculate the constant in the equation: pressure × volume = constant constant = 101 000 x 12 = 1,212,000 [3 marks] (d) The teacher pulled the plunger slowly outwards and the gas expanded. The new volume of the gas was 24 cm3. Calculate the new pressure of the gas. pressure = constant/volume pressure = 1,121,000/24 pressure = 50,500 [3 marks] (e)Tick the change occurs when the plunger is pulled slowly outwards.
[1 mark] [10 Marks TOTAL] |
Follow me...
|