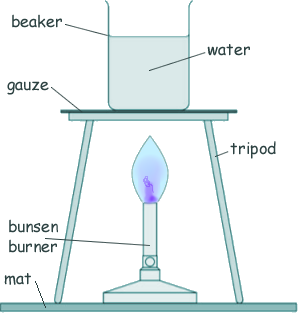
Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat Questions - GCSE standard Q11. The diagram shows a bunsen burner heating some water in a beaker. Eventually the water changes into steam.
(a) Explain how the internal energy of the water changes as it is heated from 20 °C to 25 °C The mean kinetic energy of the particles in the water (the water molecules) increases
[2 marks] (b) Choose one of the sentences below to explain how is the particle model can be used to explain the difference in density between a liquid and a gas. Tick your choice.
[1 mark] (c) Brad measured the mass of boiling water that was turned into steam in five minutes. Explain how the he could use this information to estimate the power output of the bunsen burner in watts. Energy given to water E = mL where
The power output of the bunsen burner (W) = energy transferred to the water (J)/ time of transfer (s) P = E/t P = m L/t As the time interval is 5 minutes t = 60 x 5 = 300s Therefore P = m L/300 [4 marks] (7 marks total) |
Follow me...
|