GCSE Questions: Forces Q29. The thinking distance and braking distance for a car vary with the speed of the car. (a) Explain the effect of two other factors on the braking distance of a car. Do not refer to speed in your answer.
- the examiner looks for relevant points - but also for a logical sequence... It is not just a 'tick fest' - but a marker does look to see how many relevant points you have made, then considers how you have strung them together to put your answer into a 'level'
Indicative content:
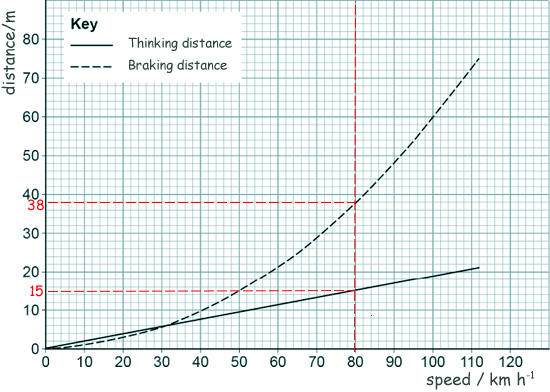
[4 marks] (b) The mean braking force on a car is 7200 N. If the car has a mass of 1600 kg calculate the deceleration of the car. F = ma 7200 = 1600 x a a = 7200/1600 a = 4.5 [4 marks] (c) The graph below shows how the thinking distance and braking distance for a car vary with the speed of the car.
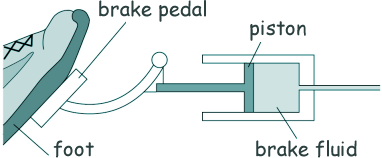
Determine the stopping distance when the car is travelling at 80 km/h. Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance Stopping distance = 15 Stopping distance = 53 m [3 marks] (d) The diagram shows part of the braking system for a car.
When the brake pedal is pressed, a force of 60 N is applied to the piston. The pressure in the brake fluid is 120 kPa. Calculate the surface area of the piston. Give your answer in standard form to 2 sf. Pressure = Force/Contact Area P = F/A 120 x 103 A = 60/(120 x 103) A = 5.0x 10-4 [5 marks]
[16 Marks TOTAL] |
Follow me...
|