GCSE Level Questions: Transformers
Q10. The diagram shows a portable power supply.
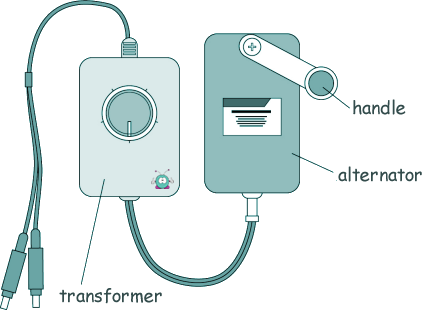
(a) The portable power supply has an alternator connected to a transformer.
The transformer can be adjusted to have different numbers of turns on the secondary coil.
Suggest why.
It is useful to vary the output potential difference  so that you don't need a different generator for each type of device.
so that you don't need a different generator for each type of device. 
[2 marks]
(b) A lamp is connected to the power supply.
The lamp requires an input potential difference of 5.0 V.
The alternator generates a potential difference of 1.5 V.
The primary coil of the transformer has 150 turns.
Calculate the number of turns needed on the secondary coil.
Ns/Np = Vs/Vp
Ns = Vs Np/Vp
Np = 150
 Vp = 1.5 V
Vp = 1.5 V 
Ns = 5.0 x 150/1.5 
Ns = 500 
[3 marks]
(c) The diagram below shows the inside parts of the alternator.
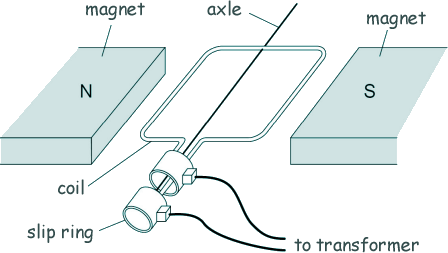
The handle of the alternator is turned, causing the coil to rotate.
(i) Explain why an alternating current is induced in the coil.
The coil moves through the fixed magnetic field from the magnet, and so the alternator coil cuts through the magnetic field lines.  A potential difference is therefore induced across the coil
A potential difference is therefore induced across the coil  and as there is a complete circuit, a current is induced in the coil.
and as there is a complete circuit, a current is induced in the coil.  The magnitude of the current varies acording the the orientation of the coil and the speed of rotation.
The magnitude of the current varies acording the the orientation of the coil and the speed of rotation.  Every half turn the potential difference reverses direction so every half turn the current changes direction making the current an alternating current.
Every half turn the potential difference reverses direction so every half turn the current changes direction making the current an alternating current. 
[5 marks]
(ii) Suggest the purpose of the slip rings.
The slip rings stop the wires from twisting together, providing a continuous/moveable contact/connection (between the coil and the transformer/contacts/brushes). 
[1 mark]
(iii) The alternator from the portable power supply is disconnected from the transformer and lamp. Explain why the handle of the alternator becomes much easier to turn.
After disconnection there is no induced current  so no magnetic field is produced around the coil
so no magnetic field is produced around the coil  opposing its movement. Therefore the operator no longer encounters opposition to the movement of the coil.
opposing its movement. Therefore the operator no longer encounters opposition to the movement of the coil.
[3 marks]
(Total 14 marks)








