Thermistor Questions
Q2.
(a) A student wishes to investigate how the resistance of a thermistor changes with temperature.
(i) Draw a labelled diagram of a suitable circuit that would enable the student to measure the resistance of the thermistor.
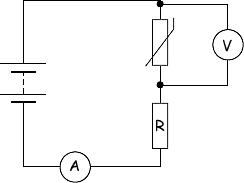 working circuit including:
working circuit including:
 power supply and thermistor
power supply and thermistor 
 voltmeter and ammeter or ohm meter
voltmeter and ammeter or ohm meter 
(2 marks)
(ii) Describe the procedure the student would follow in order to obtain accurate and reliable measurements of the resistance of the thermistor at different temperatures.
High Level (Good to excellent): 5 or 6 marks
The information conveyed by the answer is clearly organised, logical and coherent, using appropriate specialist vocabulary correctly. The form and style of writing is appropriate to answer the question.
To be included:
- the thermistor is connected in a suitable circuit with voltmeter and ammeter (or ohmmeter).
- details given of how the thermistor is heated in a beaker of water or a water bath and a thermometer is used to measure the temperature at small regular intervals.
- stating that the resistance is found at various temperatures either directly with an ohmmeter or by dividing voltage by current.
Ideally included:
- mention that the water must be stirred to ensure that the thermistor is at the temperature measured by the thermometer.
- give some indication of the range of temperatures to be used.
- repetition of whole experiment.
- plotting a graph of resistance against temperature.
Intermediate Level (Modest to adequate): 3 or 4 marks
The information conveyed by the answer may be less well organised and not fully coherent. There is less use of specialist vocabulary, or specialist vocabulary may be used incorrectly. The form and style of writing is less appropriate.
Low Level (Poor to limited): 1 or 2 marks The information conveyed by the answer is poorly organised and may not be relevant or coherent. There is little correct use of specialist vocabulary. The form and style of writing may be only partly appropriate.
(6 marks)
(b) The diagram below shows a thermistor connected in series with a resistor, R, and battery of EMF 6.0 V and negligible internal resistance.
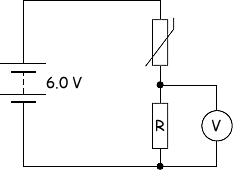
When the temperature is 50 °C the resistance of the thermistor is 1.2 kΩ. The voltmeter connected across R reads 1.6V.
(i) Calculate the pd across the thermistor.
6.0 - 1.6 = 4.4 V 
(1 mark)
(ii) Calculate the current in the circuit.
V = IR
I = V/R
I = 4.4/1200
I = 3.7 x 10-3 A 
(1 mark)
(iii) Calculate the resistance of R quoting your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
I = 3.67 x 10-3 A
V = 1.6 V
V = IR
R = V/I = 1.6/(3.67 x 10-3)
R = 436 Ω 
R = 440 Ω 
(to correct number of significant figures)
(2 marks)
(c) State and explain the effect on the voltmeter reading if the internal resistance of the battery in the circuit in part (b) was not negligible.
The terminal pd/voltage would be lower  as there would be 'lost volts' due to a potental drop across the internal resistance of the cell.
as there would be 'lost volts' due to a potental drop across the internal resistance of the cell.
Hence the pd/voltage across the resistor will decrease 
(2 marks)
(Total 14 marks)


