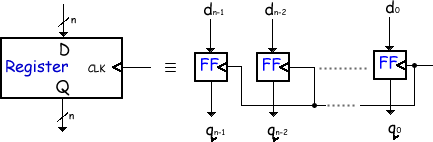
Registers In electronics a 'register' stores and or handles digital data. They are the 'holding areas' your processor uses to do arithmetic and logical calculations. The output from a register is a series of high and low voltages that correspond to binary code. Word size is related to the output capabilities of a processor's registers; it is a computer's preferred size for moving units of information around. The computer views memory as a sequence of words numbered from zero up to some large value dependent on your memory size. A simple register
This register is equivalent to n flip-flops. Each flip-flop stores one bit of information. The register holds the whole word - a binary number made up of n bits. |
Follow me...
|