|
Analogue
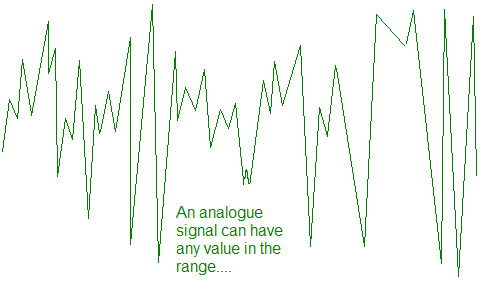
vs digital signals  Click here for a video showing the difference between analogue and digital recordings Analogue signals contain all the information as a continuously varying wave - such as on an oscilloscope screen when you speak into a microphone connected to it. Analogue means that the signal can take on any value (within the limits set by the recording equipment and the transmitter). Analogue means that the original information is retransmitted to the receiver/listener without any manipulation. For example the sound from an orchestra will consist of many different instruments playing many different notes at the same time. The human ear can distinguish all this and make sense of it even though the sound wave received by the microphone will simply be a complete combination of all these sounds. It is this combination of sounds that is transmitted to your radio or television as an analogue wave.
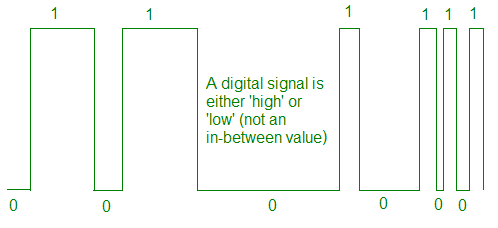
The disadvantage of analogue signals is that any 'noise', interference, added to the signal at any point cannot be removed from the audio signal and this degrades the audio quality of the signal or causes 'hiss'. Digital signals are a series of pulses - either high or low - on or off - sometimes expressed as binary code 1s and 0s. The sound of an orchestra has to be encoded to digital form before it can be transmitted and has to be decoded back to the analogue sound wave before the listener can make sense of it.Each of the analogue values is coded for in digital. So a digital pattern codes whether a particular frequency of sound is to be reproduced at what moment of time. A whole series of digital codes is therefore built up for a single analogue wave - it is then possible if enough coded information is taken to accurately reproduce the information prefectly. 'Digital' therefore means that the original recorded information has been juggled about with to enable it to be preserved without any loss of quality during transmission.
The advantage of digital signals is that
The other advantage of digital signals is that they can be sent directly to computers which use digital systems themselves. The signals from a satellite are digital. They use a system called 'packet switching' which is the same as used in computer networks and for the internet. This system is particularly effective for dealing with noise elimination. |
Follow me...
|