Nuclear Fission
Q3. A rod made from uranium-238 ( ) is placed in the core of a nuclear reactor where it absorbs free neutrons. When a nucleus of uranium-238 absorbs a neutron it becomes unstable and decays to neptunium-239 (
) is placed in the core of a nuclear reactor where it absorbs free neutrons. When a nucleus of uranium-238 absorbs a neutron it becomes unstable and decays to neptunium-239 ( ), which in turn decays to plutonium-239 (
), which in turn decays to plutonium-239 ( ).
).
(a) Write down the nuclear equation that represents the decay of neptunium-239 into plutonium-239.

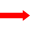
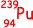 +
+  +
+ 



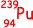 +
+ 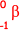 +
+ 
[2 marks]
(b) A sample of the rod is removed from the core and its radiation is monitored from time t = 0 s. The variation of the activity with time is shown below:
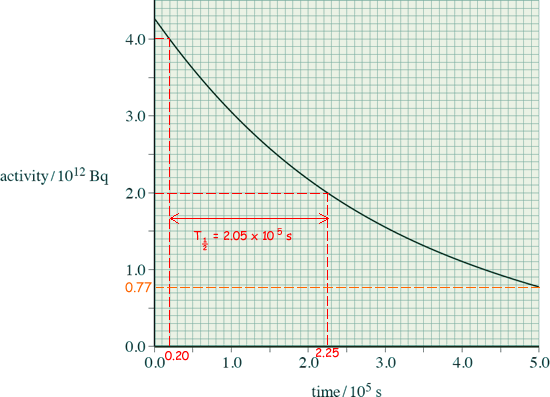
(i) Show that the decay constant of the sample is about 3.4 × 10–6 s–1.

T½ = ln2 / λ
λ = ln2 / T½
From the graph:
T½ = (2.0 → 2.1) x 105 s 
λ = (3.3 → 3.5) x 10-6 s-1 

You could substitute two points taken from the graph into A = Aoe-λt
[2 marks]
(ii) Assume that the activity shown in the graph above comes only from the decay of neptunium.
Estimate the number of neptunium nuclei present in the sample at time t = 5.0 × 105 s.
A = Nλ
N = 0.77 x 10
12
/ 3.4 x 10-6
N = (2.2 → 2.4) x 1017nuclei 

You could calculate it by using No = Ao/λ then use N = Noe-λt
[1 mark]
(c)
(i) A chain reaction is maintained in the core of a thermal nuclear reactor that is operating normally.
Explain what is meant by a chain reaction, naming the materials and particles involved.
 A chain reaction happens when the product of a reaction is that which initialises it in the first place.
A chain reaction happens when the product of a reaction is that which initialises it in the first place.
A uranium–235 nucleus captures a neutron  and undergoes fission (It splits into two smaller nuclei, called fission fragments (NOT daughter nuclei!) and releases neutrons when it splits.
and undergoes fission (It splits into two smaller nuclei, called fission fragments (NOT daughter nuclei!) and releases neutrons when it splits.
At least one of these neutrons produced in the original reaction go on to cause further fissions , thereby causing a chain reaction.
, thereby causing a chain reaction.
[2 marks]
(ii) Explain the purpose of a moderator in a thermal nuclear reactor.
 A moderator slows down (reduces the kinetic energy of) neutrons produced in a fission reaction.
A moderator slows down (reduces the kinetic energy of) neutrons produced in a fission reaction.  These neutrons are travelling too quickly to be efficiently absorbed by a uranium nucleus therefore the moderator slows them down so that they can be easily absorbed by the uranium nuclei.
These neutrons are travelling too quickly to be efficiently absorbed by a uranium nucleus therefore the moderator slows them down so that they can be easily absorbed by the uranium nuclei. 
[2 marks]
(iii) Substantial shielding around the core protects nearby workers from the most hazardous radiations. Radiation from the core includes α and β particles, γ rays, X–rays, neutrons and neutrinos.
Explain why the shielding becomes radioactive.
 Neutrons from the reaction vessel are absorbedby the nuclei in the shielding
Neutrons from the reaction vessel are absorbedby the nuclei in the shielding  converting the nuclei of the shielding into unstable isotopes
converting the nuclei of the shielding into unstable isotopes which emit radioactive particles.
which emit radioactive particles.
[2 marks]
(Total 11 marks)
