6.2.1
Point and spherical charges |
(a) electric fields are due to charges
|
 |
(b) modelling a uniformly charged sphere as a point
charge at its centre |
(c) electric field lines to map electric fields |
(d) electric field strength;
E = F/Q
|
6.2.2
Coulomb's law |
(a) Coulomb's law;
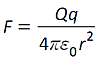
for the force between two point charges |
You will also require knowledge of section 3.2 |
(b) electric field strength
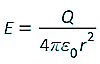
for a point charge |
| (c) similarities and differences between the gravitational field of a point mass and the electric field of a point charge |
Link to section 5.4 |
| (d) the concept of electric fields as being one of a number of forms of field giving rise to a force. |
6.2.3
Uniform electric field |
(a) uniform electric field strength;
E = V/d
|
|
(b) parallel plate capacitor; permittivity;
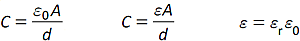
Learners are not expected to know why the relative permittivity ε≥ 1 |
(c) motion of charged particles in a uniform electric field. |
6.2.4
Electric potential and energy |
(a) electric potential at a point as the work done in bringing unit positive charge from infinity to the point;
electric potential is zero at infinity |
|
| (b) electric potential
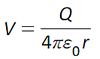
at a distance r from a point charge;
changes in electric potential |
|
| (c) capacitance
C = 4πε0R
for an isolated sphere
Derivation of this is expected from the equation for electric potential and Q = VC. |
|
(d) force–distance graph for a point or spherical charge;
work done is area under graph. |
|
| |
(e) electric potential energy
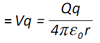
a distance r from a point charge Q. |
|


