The Gamma Camera
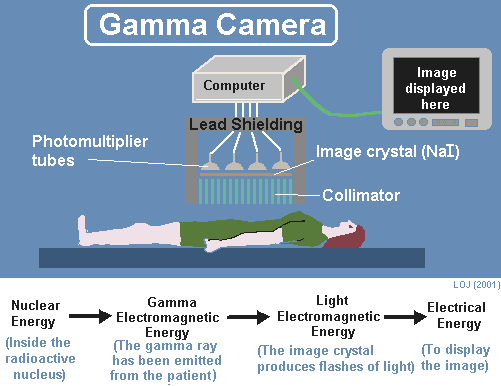
A patient is injected with a radioactive tracer that emits gamma rays. The gamma ray is electromagnetic radiation of very high penetration power. Therefore more rays exit the body and are available for detection than interact with the patient's tissue. These can be detected by a gamma camera and the concentration of radioactive tracer in various parts of the body can be ascertained. Gamma rays cannot be focused by refraction (like light rays can be) therefore a lead collimator is used to direct rays from a point on the patient towards a single point on a sodium iodide crystal. The collimator absorbs γ-rays emanating from other parts of the body before they activate the crystal ensuring that only rays from the relevant part of the body hit the crystal A crystal of sodium iodide fluoresces when a gamma ray interacts with one of its orbital electrons, promoting it to a higher energy level. On its return to ground state a photon is emitted. If this energy is in the visible region a flash of light is seen. This light is detected
using a photomultiplier and changed
into an electrical output so that it can be displayed on a monitor.The
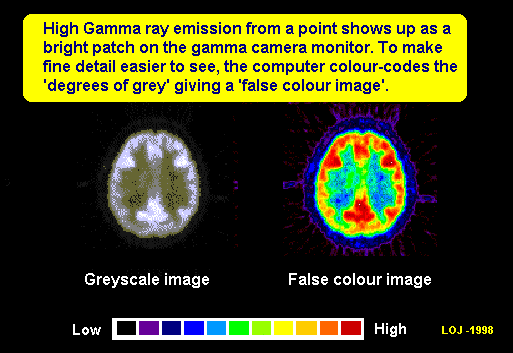
electrical output can be translated into colour coded graphical display
using electronic circuitry and the camera display can be made on a monitor
and videoed. Hard copies of the scans can then be taken and compared.
The electrical output can be translated into colour coded graphical display
using electronic circuitry.
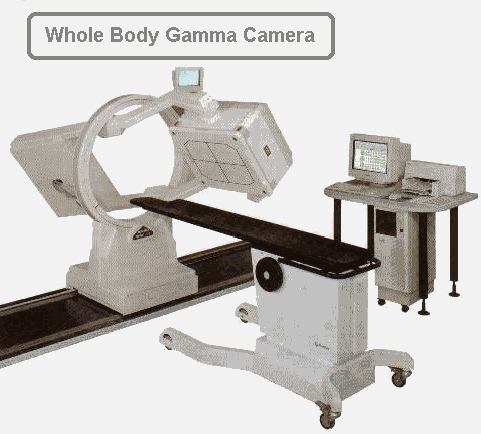
Above image taken from: http://www.sielimaging.com/images/gamma_cam1.jpg
|
Follow me...
|